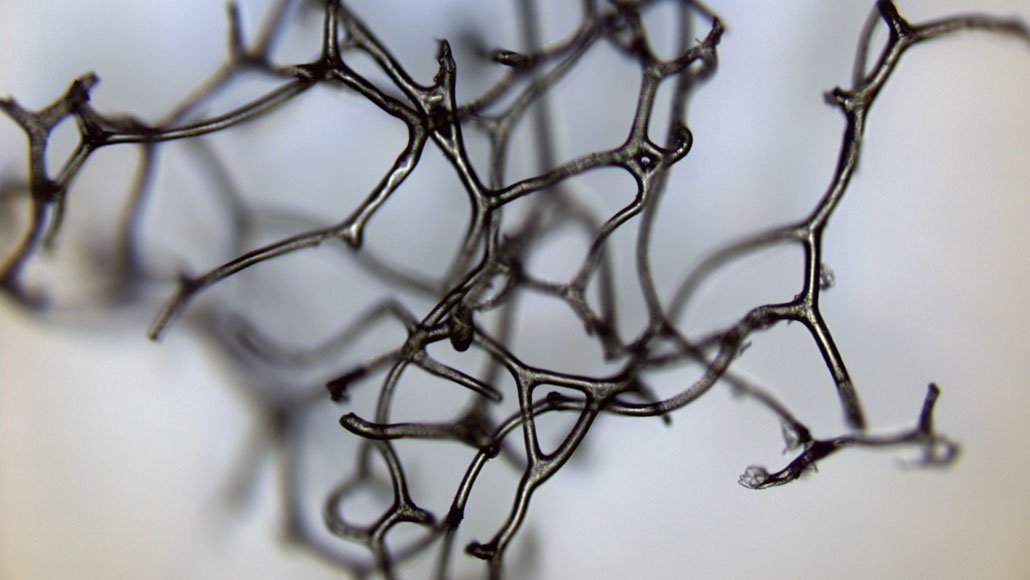
Pale, wormlike tubes in 890-million-year outdated rock could also be historic sea sponges, a brand new examine concludes. If confirmed, that controversial declare would push again the origin of the earliest sponges by about 350 million years and make the tiny squiggles the oldest identified fossils of animals, by far.
Crucially, these fossils would indicate that animals emerged in environmental situations beforehand thought unworkable for animal life, geologist Elizabeth Turner experiences July 28 in Nature.
Early in Earth’s historical past, the ocean largely lacked oxygen. It wasn’t till a big pulse of the fuel to the ambiance about 800 million to 540 million years in the past, referred to as the Neoproterozoic Oxidation Occasion, introduced atmospheric oxygen ranges to inside 10 to 50 % of recent ranges, boosting the quantity of oxygen in floor ocean waters (SN: 12/11/19). “However sponges are completely different from different animals,” says Turner, of Laurentian College in Sudbury, Canada. “Some sponges within the fashionable world and within the rock report are identified to be tolerant of comparatively low oxygen relative to fashionable ocean ranges.”
Till now, the earliest, unambiguous fossils of sponges date to about 540 million years in the past to the start of the Cambrian Interval, when an excessive burst within the evolution of animal variety occurred (SN: 7/29/13). Another animals are identified from only a bit earlier, however go an excessive amount of additional again in time and identities turn into much less clear (SN: 3/9/15). Primarily based on genetic information and their relative simplicity, sponges are typically thought to have been the earliest type of animal life.
Signal Up For the Newest from Science Information
Headlines and summaries of the newest Science Information articles, delivered to your inbox
However some scientists aren’t satisfied that the newly described tubes are sponge fossils. “Organisms from wherever on the tree of life could make wiggly, little [branching and rejoining] constructions,” says Jonathan Antcliffe, a paleobiologist on the College of Lausanne in Switzerland. The fossils lack options comparable to mineralized skeletal elements known as spicules that may determine the creatures as sponges, he says.
What’s extra, the discovering “doesn’t match with every part we learn about the entire [ocean] ecosystem” with regard to nutrient, biomineral and oxygen availability earlier than the Cambrian Interval, Antcliffe says. “Every thing we all know concerning the Earth’s oceans on this interval of time tells us that animals originated round 540 [to] 550 million years in the past. It’s a legion of proof, and to overturn such an enormously sturdy paradigm, you want greater than ‘is perhaps a sponge.’”
Turner first discovered the community of tubes in 1992 in rocks from the traditional Little Dal cyanobacteria reef in Canada’s Mackenzie Mountains. “I discovered this factor that was completely misplaced,” she says. “It was rather more advanced by way of its construction than something that might be made by cyanobacteria.”
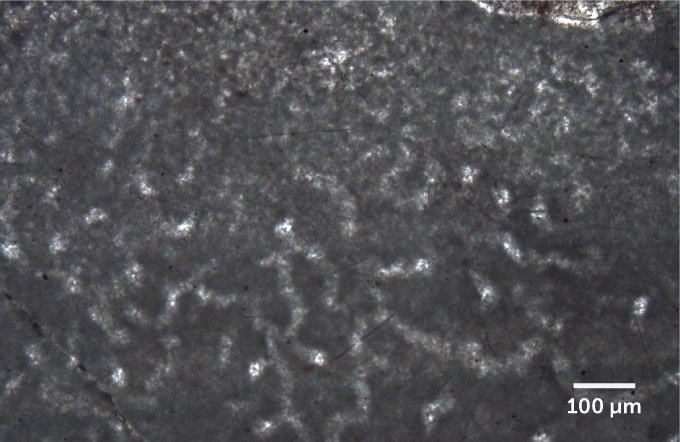 This microscope picture exhibits the pale, wormlike tubes of putative fossils of historic sea sponges, present in 890-million-year outdated rock.E.C. Turner/Nature 2021
This microscope picture exhibits the pale, wormlike tubes of putative fossils of historic sea sponges, present in 890-million-year outdated rock.E.C. Turner/Nature 2021
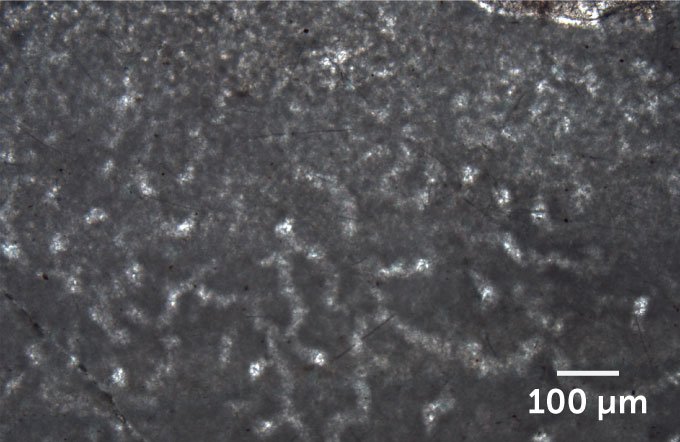 This microscope picture exhibits the pale, wormlike tubes of putative fossils of historic sea sponges, present in 890-million-year outdated rock.E.C. Turner/Nature 2021
This microscope picture exhibits the pale, wormlike tubes of putative fossils of historic sea sponges, present in 890-million-year outdated rock.E.C. Turner/Nature 2021
She would have reported the curious squiggles then, however with out a lot else to tie them to sponges apart from a basic resemblance, Turner moved on. However after newer analysis confirmed that sponges might be preserved in rock equally to the Little Dal’s pallid wiggles, she returned to her discover.
Turner argues that many fashionable sponges don’t have spicules and that the newly described fossils could also be comparable. And he or she means that sponges predating the Neoproterozoic Oxidation Occasion might have scraped out an existence in “oxygen oases” alongside microbial reefs, dwelling in holes and reef flanks and never competing with cyanobacteria for house.
It’s potential that early sponges emerged a lot sooner than the remainder of animal life and remained in a sort of “evolutionary stasis” in low-oxygen situations, she says, with the evolution of later, extra advanced animals having to attend till the fuel turned extra plentiful.
Scientists have identified about odd forms of fossils within the Little Dal reef for some time, says James Schiffbauer, a paleobiologist on the College of Missouri in Columbia who wasn’t concerned within the analysis. And “we’ve anticipated from molecular clocks that sponges ought to be current earlier within the Neoproterozoic [Era],” he provides, referring to genetic analyses that estimate that sponges advanced nicely earlier than the Cambrian Interval. “It has simply been a matter of discovering them in the event that they have been certainly preserved.”
Future analysis might assist verify the fossils’ identification. Turner plans to work extra with the traditional tubes, including that extra solutions might come from wanting in the fitting locations. “We have to be in search of comparable materials with a extremely open thoughts in rocks of comparable age, and we have to be in search of extra advanced animal proof in them as nicely,” relatively than simply less complicated organisms like microbes.



